Molecular orbital (M .O) theory
Molecular orbital (M.O) theory :
Introduction:Based on wave mechanics, Hund and Mulliken published their molecular orbital theory in 1932. Molecular orbital theory was established on the linear combination of atomic orbital (LCAO).
So it is called LCAO-M.O theory. Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the
electronic structure of molecules.
Electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nucli in the whole molecule.
Significance of M.O theory
(I)Molecular orbital theory explain correctly the magnetic properties of molecules which would not be explain valence bond theory.
(II)Valence bond theory does not explain about the concept of fractional bond formed in the molecule which proved by molecular orbital theory.
(II) Why He2 molecule does not exist, valence bond theory is unable to explain it.
(IV)How the atomic orbital in a molecule surround by two or more atoms containing valence electron ,can not explain VBT but can explain M.O.T
The basic principles of m,o theory are as follows
(I)When nuclei of two atoms come close to each other, their
atomic orbitals interact leading to the formation of molecular orbitals.
The atomic orbitals of the atom in a molecule completely lose their identity after the formation of molecular orbitals.
The atomic orbitals of the atom in a molecule completely lose their identity after the formation of molecular orbitals.
(II) Molecular orbitals are formed by the linear combination of atomic orbitals . Two atomic orbital of definite
energy combine to form molecular orbital. e.g 1S orbital combine with another 1S orbital.
(II)n-no. of A.O combined to form n-no of M.O .One half of
these M.O with lower energy than A.O are
bonding m.o and another half with higher energy than A.O are ABMO.
(IV) The shape of M.Os depends on the shape of concern A.OS
.
(V)Each M.O is described by a wave function Ѱ , known
as M. wave function.
(VI)the density of electronic charge in BMOs is greater than
ABMOs
.
(VII)Each M.O wave function (Ψ ) is associated with a set of
quantum no. which determine the energy and shape of the M.O.
(VIII) Like A.O,electron entered the M.O according to
Aufbau principle .
(IX)Like A.O , one M.O occupied maximum two electron with
opposite spin according to pauling exclusion principle.
(X)The electron entered the M.O with equal energy gradually
according to Hunds rule of maximum multiplicity .
Formation of molecular orbitals
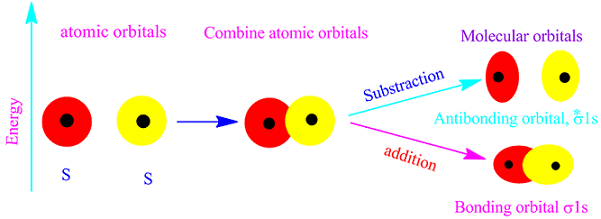
According to molecular orbital theory, the molecular orbitals are formed by the linear combination of atomic orbitals, LCAO.
Since electron have wave nature,so the wave function of two atomic orbitals may combine either additively or sudstractively.
Since electron have wave nature,so the wave function of two atomic orbitals may combine either additively or sudstractively.
Article summary :
What is molecular orbital theory ?
What is the significance of M.O theory ?

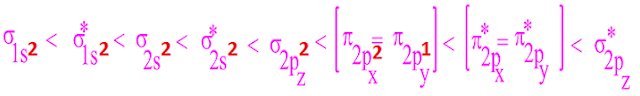






No comments