Tuesday, June 30, 2020
What are the main causes of acid rain in environmental chemistry?
Friday, June 26, 2020
[Ni (NH3)6]2+paramagnetic while [Ni (CN) 6]4-diamagnetic
Why is [Ni (NH3)6]2+paramagnetic while [Ni (CN) 6]4-diamagnetic?
Wednesday, June 24, 2020
What are the common uses of hydrochloric acid in chemistry
What are the common uses of hydrochloric acid in chemistry?
Friday, June 12, 2020
Hydroiodic acid-formula-properties-uses with pH calculation
What is hydroiodic acid in halogen chemistry?
Hydroiodic acid is an important chemical in chemistry, especially in inorganic chemistry. It is slightly polar [ionic character 5%] covalent molecule with chemical formula, HI.
The others name of hydroiodic acid is iodane,
hydrogen iodide, hydriodic acid, hydronium iodide etc.
Friday, June 5, 2020
[FeF6]3– ion paramagnetic while [Fe(CN)6]4–ion diamagnetic
Why is [FeF6]3– ion paramagnetic while [Fe(CN)6]4–ion diamagnetic ?
Thursday, June 4, 2020
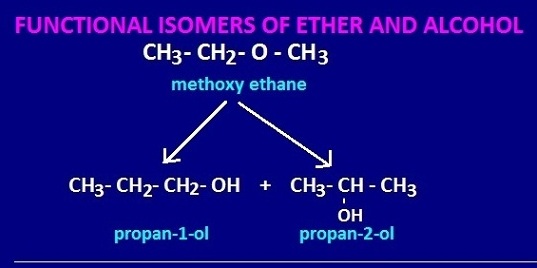
Structural formula and f IUPAC name of functional isomer of CH3-CH2 – O – CH3
Structural formula and IUPAC name of functional isomer of CH3-CH2 – O – CH3.
Wednesday, June 3, 2020
IUPAC name and structural formula of beta methyl butyric acid
IUPAC name and structural formula of beta methyl butyric acid
Beta
methyl butyric acid is an example of aliphatic mono carboxylicacid. It is a branch chain carboxylic acid with functional group –COOH.
The carbon atom which attached with –COOH group is called alpha carbon and
the carbon atom which directly attached with the alpha carbon atom is called
beta carbon atom.
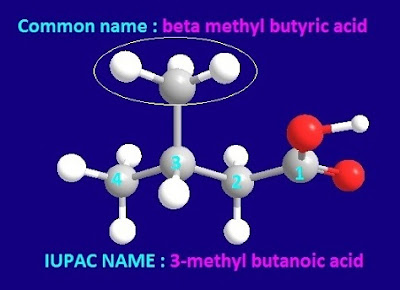 |
So, the structural formula of beta methyl butyric acid is shown below.
According to IUPAC rules, in the nomenclature of
aliphatic carboxylic acid, the carbon atom of carboxylic group will get the
numbering first and then rest of the carbon of the long chain will get their
number.
In the naming of carboxylic acid the rule is, alkane –ane +an + oic acid. If the compound contains branch, then the IUPAC name will
start with naming the concern branch first.
So, the IUPAC name of beta methyl butyric acid should
be, 3-methyl butanoic acid.
Summary:
What is structural formula of beta methyl butyric acid ?
What is the IUPAC name of beta methyl butyric acid ?
What is full form of IUPAC ?
Read more: activating groups with application





![[FeF6]3– ion paramagnetic while [Fe(CN)6]4–ion diamagnetic [FeF6]3– ion paramagnetic while [Fe(CN)6]4–ion diamagnetic](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEirxLJKrZb7_8hPGbgWSrkPE2VURnAXdVYxBnbxcGW40A6D00VzBWpGCsPo0L3COwbdUqcrie3P9GZ7E-gPdnte7UzZbzzXwovbr5LpG_t5BVhgeK0LqTPD2C6BB5yNLgYhOCNRi-Bo3B4/w640-h329/D-octa-splitting.jpg)