What is ammonia (NH3)?
What is ammonia (NH3)?
Ammonia is a chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with molecular formula NH3. There are three hydride of nitrogen.
Out
of them, ammonia is the main hydride of nitrogen. Ammonia is also known as
nitrogen tri hydride or trihydrido nitrogen.
It is a colorless with intense pungent smelling gas. Ammonia is lighter than air with vapour density 8.5. Ammonia itself is not combustible and does not help the combustion of others.
It is easily converted into colorless liquid at 283K temperature under 6 atmosphere pressures.
The melting point of solid ammonia is 195.3K and the boiling point of liquid ammonia is 239.6K.
Liquid ammonia dissociates in very small amounts and remains in the ionized state.
2NH3 ⇌ NH4+ + NH2-
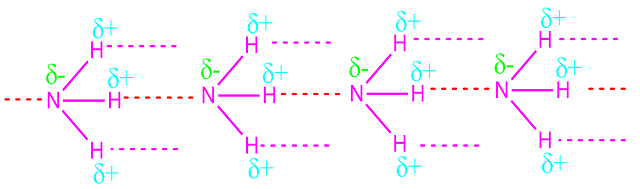
Ammonia is super soluble in water due to formation of hydrogen bond between water and ammonia molecules. About 1300 cc of ammonia gas is dissolved in 1 cc water at NTP.
The concentrated aqueous solution of ammonia is known as liquor ammonia. Liquor ammonia contains 35% ammonia. Its specific density relative is 0.88. Liquid NH3 is a non aqueous solvent.
The aqueous solution of ammonia is mild basic in nature. Its aqueous solution turns red litmus into blue.
As the latent heat of vaporization of liquid ammonia is very high, it is widely used for cooling.
In
the liquid and solid state, ammonia molecules
are associated through the formation of inter molecular hydrogen bonds.
For this reason, the melting point and boiling point of ammonia
molecules are higher than the expected value.
What is ammonia formula?
The
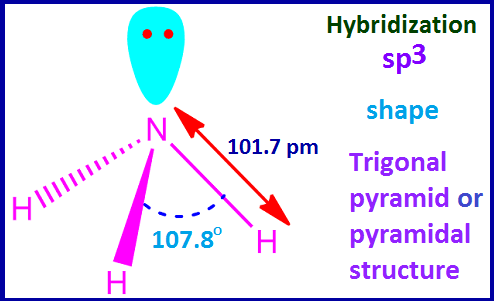
chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. The central nitrogen atom is sp3
hybridized. So the shape of the NH3 molecule should be tetrahedral.
But
N-atom contains one lone of electron. Hence according VSEPR theory ammonia
molecule exists in pyramidal structure.
The
H –N –H bond angle is 107.8ᵒ instead of 109.28ᵒ. The bond length of each N–H
bond is 101.7 pm.
Preparation of ammonia
Ammonia
may be prepared in different methods. There are two important methods for
preparation of ammonia. One is laboratory and the other is industrial methods.
Laboratory
method for ammonia preparation:
In
the industry, ammonia is produced by heating a mixture of NH4Cl and dry lime or
burnt lime.
In this case ammonia is prepared
by heating a mixture of one part NH4Cl with three parts of calcium hydroxide.
Industrial method for NH3
preparation (Haber’s process):
Ammonia
is prepared industrially by Haber’s
process. In this method, one volume of
nitrogen gas reacts with three volumes of hydrogen gas to form two volumes of
ammonia gas.
In this reaction iron dust is used as a
catalyst and molybdenum dust is used as a promoter. The reaction is reversible and exothermic.
The
reaction takes place at an optimum temperature of 700 K under 200 atmospheric
pressures.
Ammonia pH
Ammonia is highly soluble in water. It dissolves in water and form ammonium hydroxide which is also known as ammonia liquor, aqueous ammonia, NH3 water etc.
However, ammonia is a weak base. So the pH value of aqueous ammonia does not determined directly.
There are two indirect methods for determination of pH of aqueous ammonia or ammonium hydroxide.
The
first method is determination of pH of weak base (NH4OH) by the dissociation
constant (Kb) and the concentration of NH4OH by using the given following
equation.
pH = 14 – 1/2pKb + 1/2logc
The second method is determination of pH of weak base (NH4OH) by the degree of dissociation and the concentration of NH4OH.
In this method, pH = 14 + log [OH-]
The ionization of NH4OH is, NH4OH = NH4+ + OH-
Now, in 1(M) ammonia solution, about 0.42% of the ammonia is converted to ammonium hydroxide.
Therefore, the [NH4+] = [OH−] = 0.0042 (M).
Hence, pH = 14 + log [OH−] = 14 + log[0.0042]
=14 – 2.374 =11.6
Therefore,
the pH of 1(M) ammonium hydroxide is 11.6.
What are uses of ammonia?
Use of ammonia as
Fertilizers
The most important use of ammonia is as a nitrogenous fertilizer.
For example, ammonia is used in
the preparation of nitrogenous fertilizers like urea, ammonium sulphate,
ammonium nitrate, calcium ammonium nitrate, ammonium phosphate etc.
Precursor of nitrogenous compounds
Ammonia is used as precursor directly or indirectly of most nitrogen-containing compounds. Generally all synthetic nitrogen-containing compounds are derived from ammonia.
An important derivative is nitric acid via Ostwald’s process by the oxidation of NH3 with air over a Pt catalyst at 700-800ᵒC temperature under 9 atmosphere pressures.
This nitric acid is used for the production of fertilizers, explosives and many organo nitrogen compounds.
Ammonia is also used to prepare hydrazine, hydrogen cyanide, phenol, hydroxylamine, amino acid, acrylo nitrile etc compounds via different synthesis methods.
Ammonia can also be used to make compounds in reactions which are not specifically named.
Examples
of such compounds are ammonium perchlorate, HCONH2, N2O4, alprazolam,
ethanolamine, ethyl carbamate, (CH2)6N4, and NH4HCO3.
Use of ammonia as a freezer
Liquid ammonia is used as an important freezer due to high enthalpy of vaporization.
For
this reason, liquid ammonia is widely used as a freezer in the preparation of
ice and in the preservation of vegetables, fruits, etc. in the cold storage.
Use of ammonia as a cleaner
Household ammonia is a 5% - 10% solution of NH3 in water, and is used as a general purpose cleaner for many surfaces.
Because ammonia results in a relatively streak-free shine, one of its most common uses is to clean glass, porcelain and stainless steel.
It is also frequently used for cleaning ovens and soaking items to loosen baked-on grime.
Ammonia
is also used in the preparation of smelling salts and for cleaning oily
substances or grease.
Use as laboratory reagents
Aqueous solutions of ammonia that is ammonium hydroxide are used as important reagents in the laboratory for qualitative and quantitative analysis.Anhydrous liquid ammonia is used as non aqueous solvent.
Use of ammonia in fermentation
16%-25%
solutions of ammonia are used in the fermentation industry as a source of
nitrogen for microorganisms and to adjust pH during fermentation.
Antimicrobial agent for food products
Approximately 125 years ago, it was known that ammonia was strongly antiseptic and it used to preserve beef tea.
In one study, anhydrous NH3 destroyed 99.99% of zoonotic bacteria in 3 types of animal feed.
Now anhydrous NH3 is used
commercially to reduce or eliminate microbial contamination of beef.
Others
uses of ammonia
Some ammonium compounds are used medicinally. Ammonia is also
used in the preparation of artificial rayon, plastic, rubber etc.
Ammonia is also used in the industrial preparation of
nitric acid in the Oswald method and sodium carbonate in the Solve method.
Toxicity of ammonia
The toxicity of ammonia solutions does not usually cause problems for humans and other mammals, as a specific mechanism exists to prevent its build-up in the bloodstream.
But the concentration solution of ammonia is harmful for human eyes. Excess ammonia can damage our eyes.
Again,
ammonia even at dilute concentrations is highly toxic to aquatic animals, and
for this reason it is classified as dangerous for the environment.
- What is ammonia (NH3)?
- What is ammonia formula?
- Preparation of ammonia
- Ammonia pH
- What are uses of ammonia?
ammonia, ammonia gas, NH3, NH3 gas, ammonia formula, use
of ammonia, ammonia pH, ammonia chemical formula, anhydrous ammonia, toxicity
of ammonia,
Read more: synthesis reactions in organic chemistry










Nice
ReplyDeleteI like your blog and it is very simple. You have shared great information with us. I want to add some value here such as Complete Ammonium Hydroxide Production ProcessWater Molecules in Ammonium Hydroxide & More About the Chemical
ReplyDeleteThank you for your kind words about my blog! I strive to keep it simple yet informative. Your desire to contribute valuable insights is appreciated. Feel free to share your expertise and enrich our community with additional knowledge. Together, we can create a more enriching experience for all readers Testing for Total Ammonia Nitrogen.
ReplyDeleteSteelman Gases Pvt. Ltd. is a trusted provider of Ammonia Gas, Ammonia Solution, Chlorine Gas , and Sodium Hypochlorite for various industries. As reliable Sodium Hypochlorite Solution Manufacturers, we ensure our products meet the highest quality and safety standards. With a focus on innovation and customer satisfaction, Steelman Gases Pvt. Ltd. is your go-to partner for top-quality Ammonia Gas, Ammonia Solution, Chlorine Gas, and Sodium Hypochlorite products.
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteSteelman Gases is a reliable industrial chemical supplier known for quality, safety, and timely delivery across India. Serving multiple sectors with advanced production standards, we ensure consistent performance and purity. As trusted Anhydrous Ammonia Manufacturers we provide safe storage, efficient distribution, and competitive pricing. We are also leading Chlorine Gas Suppliers, Sodium Hypochlorite Manufacturers, Liquor Ammonia Manufacturers, and Sulphur Dioxide Gas Manufacturers.
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteSteelman Gases is a trusted industrial chemical company delivering reliable and safe solutions across India. With modern infrastructure and strict quality control, we serve water treatment, chemical, and industrial sectors efficiently. As leading Sodium Hypochlorite Manufacturers
ReplyDeletewe ensure high purity, secure packaging, and timely supply. We are also recognized as Chlorine Gas Suppliers, Anhydrous Ammonia Manufacturers, Liquor Ammonia Manufacturers, and Sulphur Dioxide Gas Manufacturers.