Isomerism and classification of structural isomerism
What is isomerism ?
When two or more organic compounds having same molecular formula but with different chemical structure due to different arrangement of each elements in space exhibit different physical and chemical properties, then they are called isomer to each other and this phenomenon is called isomerism.
For
example, ortho xylene, meta xylene and para xylene.
What is structural isomerism ?
When
two or more isomers with the same molecular formula exhibit different physical
and chemical properties due to different bonding patterns, then they are
called structural isomers and this phenomenon is called structural isomerism.
For
example n-pentane , iso-pentane and neo-pentane.
Classification of structural isomerism.
What is functional group isomerism ?
When two structural isomers with same molecular formula but different functional group create a new type of isomerism, is known as functional group isomerism.
For example, acetic acid and methyl formate with same molecular formula C2O2H4, exhibit this type of isomerism
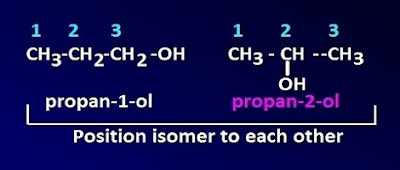
What is position isomerism ?
This
type of isomerism arises due to the different in the position of the same
functional group or atom on the carbon chain in a molecule. For example, ortho
nitro phenol, mete nitro phenol and para nitro phenol.
- What is chain isomer?
- What is ring-chain isomerism ?
- What is metamerism ?












No comments