What is dehydrogenation of alcohol reactions in organic chemistry?
What is dehydrogenation of alcohol reactions in organic chemistry?
Dehydrogenation is an important chemical reaction, usually associated with the removal of hydrogen from organic molecules. It is the opposite reaction of hydrogenation.
Dehydrogenation reactions produce aldehydes, ketones, alkenes, alkynes, polymers and aromaticand aliphatic closed chain compounds.
The
reaction takes place in the presence of a catalyst at a temperature of 300-500 ᵒC.
Dehydrogenation of aromatics and aliphatic
alcohols are mainly discussed here basically.
Dehydrogenation of alcohol reactions examples.
When alcohol vapor is passed over a heated metallic copper
catalyst at a temperature of 300 ᵒC, the alcohol is oxidized to produce
aldehydes and ketones.
Aldehydes
are produced when the primary alcohol is oxidized and ketones are produced when
the secondary alcohol is oxidized.
In this case no oxidant is used. Therefore the aldehydes and ketones
produced cannot be re-oxidized and converted into carboxylic acids
For example, formaldehyde is produced when methanol vapor
is quantitatively mixed with air or oxygen and heated at 250 ᵒC in the presence
of a catalyst.
A
mixture of silver powder and V2O5 is used as a catalyst in the reaction.
It is the dehydrogenation reaction of methanol, by which formaldehyde is
produced industrially.
Why
does 3ᵒ or
tertiary alcohol not participate in dehydrogenation reaction?
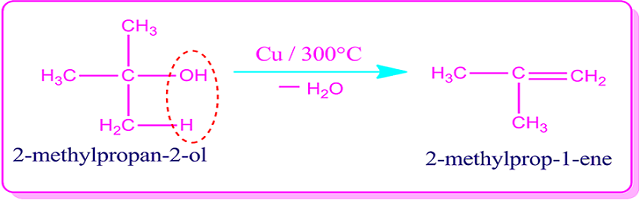
Tertiary
or 3ᵒ alcohol does not participate in the dehydrogenation reaction as no
hydrogen is added directly to the carbinol-carbon of alcohol. In this case
alkene is produced by the dehydration reaction.
What is iodo-form test for ethanol in organic chemistry?
Compounds
that contain keto-methyl group or compounds those are oxidized during reaction
to form keto-methyl group containing compounds, react with iodine in the
presence of alkali to form iodo-forms.
This
reaction is called iodo-form test. For example, ethanol is oxidized to
acetaldehyde during reactions, in which the keto methyl group is present. Hence, ethanol responds to iodo-form tests.
- What is dehydrogenation of alcohol reactions in organic chemistry?
- What is dehydrogenation of alcohol in organic chemistry?
- Dehydrogenation of alcohol reactions examples.
- What is iodo-form test for ethanol in organic chemistry?
Dehydrogenation
of alcohol reactions, dehydrogenation of alcohol, dehydrogenation of alcohol
reactions examples, iodo-form
test for ethanol,
Read more : Balancing chemical equations by oxidation method












No comments