Balancing equations chemistry by oxidation number method for class 11
Balancing equations chemistry by oxidation number method for class 11
An
important method of balancing equations of chemical reactions is the oxidation
number system. In this method, the balancing of reactions is provided by
changing the oxidation number.
In the case of the oxidation number method, an
equation of the reaction is created by first identifying the reactants and the
products.
Then
the oxidation number of the atoms of the elements in the reactant and the
product changes, they are marked and written with oxidation numbers.
The
reactant in which the oxidation number of atoms of an element decreases is
oxidant and the reactant in which the atomic number of atoms in an element
increases acts as a reducing agent.
Oxidation
and reduction are complementary to each other. This is why the decrease
increase in oxidation number has to be equal.
For this reason, symbols of oxidant and reductant are multiplied by the suitable smallest integer, so that the change
in the oxidation number of both is equal.
Due
to balancing of equations often the symbols of other participating substances
in the reaction also need to be multiplied by the appropriate number.
In
the case of acidic medium reactions, to equalize the number of oxygen-atoms,
one H2O molecule is added for each oxygen-atom on the side of the
equation where there is an oxygen-atom deficit.
In order to equalize the number of hydrogen-atoms, acid molecules are added to the side where there is a deficiency of hydrogen-atoms.
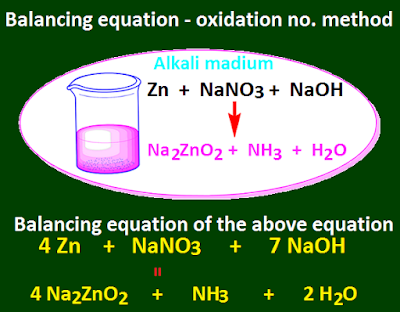
If the reaction occurs through an alkaline
medium, then in order to equalize the number of oxygen-atoms, one H2O
molecule is added for each oxygen-atom on that side of the equation where there
is an oxygen-atom deficiency and the appropriate number of alkali molecules on
the opposite side.
Again to equalize the number of hydrogen-atoms
on the side with the excess hydrogen-atoms, a suitable number of alkali molecules are added on that side and a suitable number of H2O molecules are
added on the opposite side.
The above said steps provide the balancing of
equations of chemical reaction in the oxidation number system.
The balancing of equations for chemical reactions occurring both in acids and alkalis are shown below.
In the case of equations of chemical reactions occurring with acids mediums. For example, the reaction of KMnO4 and H2O2 in the presence of H2SO4 produces K2SO4, MnSO4, H2O and O2. In this case the chemical equation is,
Now,
increase in the oxidation number of O-atoms = 0 - (- 1) = 1 unit.
Decrease in the oxidation number of Mn = +7 -
(+2) = 5 units.
Thus the total increase in the oxidations number for the two O-atoms present in the H2O2 molecule is = 2 units.
In
order to equalize the decrease and increase of the oxidation number in the reaction,
the ratio of the atomic number of KMnO4 and H2O2 in the reaction equation will
be 2: 5.
Again
2 molecules KMnO4 and 5 molecules H2O2 produce 2 molecules MnSO4 and 5
molecules O2 respectively. So the new equation
would be,
Again, three SO4 radicals are needed to
produce 1 molecule K2SO4 and 2 molecules MnSO4.
Thus, 3 molecules H2SO4 are required on the
left side of the equation. In addition, the total number of hydrogen atoms in 5
molecules H2O2 and 3 molecules H2SO4 is 16. Water is generated from these hydrogen atoms.
So,
4 H2O molecules have to be placed on the right side of the equation. Therefore,
the balancing equation is,
Again in the case of equations of chemical
reactions occurring through alkalis.
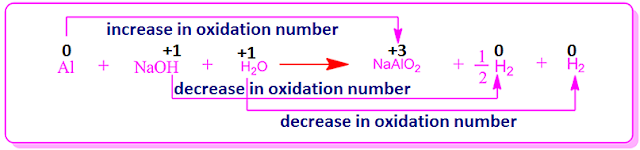
When
heated caustic soda solution is heated with Al powder, sodium aluminate and
hydrogen gas are produced. In this case, the chemical equation is,
In the reaction Al oxidizes to produce NaAlO2 and the H-atoms of both NaOH and H2O compounds reduce to form hydrogen molecules gases.
So
the new structure of the reaction must be written with a change in the
oxidation number,
Now,
increase the oxidation number of Al-atoms = (+ 3) - 0 = 3 units.
Decrease in oxidation number of one H-atom of NaOH-molecule = (+1) - (1/2 x 0) = 1 unit.
Decrease in oxidation number of two H-atoms of H2O-molecule = 2 X (+1) - (2 x 0) = 2 units.
Thus
the total decrease in oxidation number of H-atoms of 1 molecule NaOH and 1
molecule H2O = 1 + 2 = 3 units.
To equalize the decrease and increase of the oxidation number, the ratio of the number of Al-atoms, the number of NaOH molecules and the number of H2O molecules will be 1: 1: 1.
So the equation of the given reaction would
be,
Now
both sides have to be multiplied by 2 to express the number of the reactant and
the product substance with integers. So, the
balancing equation is as follows.
- Balancing equations chemistry by oxidation number method for class 11
- Balancing equations by oxidation number method simple examples
- How to balance chemical equation in chemistry?
Balancing
equations chemistry, balancing equations, balancing equations by oxidation
number method for class 11, balancing equations by red-ox method, balancing equation
in chemistry simple examples,














No comments