Polarization meaning-Ionic potential-polarizability and polarizing power
Polarization meaning in chemistry
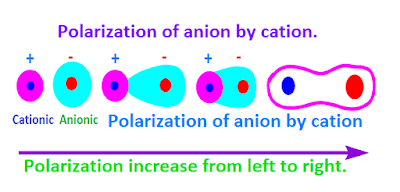
In case of ionic crystal , it has been observed that, the positive electric field of cation pull the electronic sphere of an anion from their equal distance.
But the
positive electric field of cation repulse the nucleus of anion. As a result,
the deformation of symmetric electron
charge cloud of anion by cation is called
polarization of anion.
Generally,
cation with smaller size or with high positive charge cause the high
polarization of anion.
On the other
hand, anion with large size or with high negative charge also cause the high
polarization of itself.
For example,
Al3+ ion cause the highpolarization of a particular anion than Na+ ion ,due to small size
and high charge with respect to Na+
ion.
Polarizing power and polarizability in chemistry
What is polarizing power of cation ?
The
polarizing power of cation is defined as the capability to distort the electron
charge cloud of an anion.
Now, it has
been experimentally found that, cation with smaller size or with high positive charge have its high polarizing power.
For example,
Al3+ ion have more
polarizing power than Na+ ion,
due to small size and high charge of Al3+
with respect to Na+ ion.
What is polarizability of anion in chemistry?
Polarizability is defined as the property of an anion to become polarized through
the deformation of electron charge cloud by cation.
Polarizability of an anion increase with increase in anionic size or anionic charge.
For example, the polarizability of I–
anion is higher than F – ion, due to large size of iodide
ion.
If the polarizability of an anion increase, then covalent character of the concern compound increase. Such as , AgI is more covalent than AgF.
Ionic
potential(ф) definition in chemistry
A parameter
is used to expressed the polarizing power of cation is known as ionic potential
. It is denoted by the symbol ‘ф’.
The ionic potential is defined as the ratio of cationic charge and cationic radius.
With increasing the value of ‘ф’ , the polarizing power of cation
increases. As a result, the covalent character in ionic compounds
increases.
Periodic variation of covalent character in ionic compounds.
( I )When we move from left to right
along a period, the cationic charge increases and hence cationic radius
decreases.
That is, the value of ‘ф’ increases
.Consequently, the covalent nature in
ionic compounds increases.
For example, the value of ionic potential (‘ф’)
for Na, Mg, Al increase from Na to Al . Hence, covalent character of the their
relating compound increases in the same order.
( II ) On the other hand , if we moved
from top to bottom along a group , the cationic charge remain unchanged, but due
to increase of ionic radius, the value of
‘ф’
decreases. Consequently, the covalent nature in ionic compounds increases.
For example, the order of ionic
potential (‘ф’) value of group-II elements, such as Be ,
Mg and Ca are decrease from top to bottom.
Hence covalent character of their
concerned compounds slowly decrease from top to bottom , that is from Be to Mg to Ca. Same explanation for Li , Na and K metal .
(III ) In case of different oxidationstate of same metal, the value of ‘ф’ increase with
increase in oxidation number. Consequently, the covalent character
with higher oxidation state increases.
Summary
- Polarization meaning in chemistry
- What is polarizing power of cation in chemistry
- What is polarizability of anion in chemistry
- Ionic potential(ф) definition in chemistry













No comments